Vue对象提供的属性功能
过滤器
过滤器,就是vue允许开发者自定义的文本格式化函数,可以使用在两个地方:输出内容和操作数据中。
定义过滤器的方式有两种。
使用Vue.filter()进行全局定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| Vue.filter("RMB1", function(v){
if(v==0){
return v
}
return v+"元"
})
|
在vue对象中通过filters属性来定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{},
filters:{
RMB2:function(value){
if(value==''){
return;
}else{
return '¥ '+value;
}
}
}
});
|
计算和侦听属性
计算属性
我们之前学习过字符串反转,如果直接把反转的代码写在元素中,则会使得其他同事在开发时时不易发现数据被调整了,所以vue提供了一个计算属性(computed),可以让我们把调整data数据的代码存在在该属性中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
str1: "abcdefgh"
},
computed:{
strRevs: function(){
var ret = this.str1.split("").reverse().join("");
return ret
}
}
});
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ str1 }}</p>
<p>{{ strRevs }}</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
监听属性
侦听属性,可以帮助我们侦听data某个数据的变化,从而做相应的自定义操作。
侦听属性是一个对象,它的键是要监听的对象或者变量,值一般是函数,当侦听的data数据发生变化时,会自定执行的对应函数,这个函数在被调用时,vue会传入两个形参,第一个是变化前的数据值,第二个是变化后的数据值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
num:20
},
watch:{
num:function(newval,oldval){
console.log("num已经发生了变化!");
}
}
})
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ num }}</p>
<button @click="num++">按钮</button>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
vue对象的生命周期
每个Vue对象在创建时都要经过一系列的初始化过程。在这个过程中Vue.js会自动运行一些叫做生命周期的的钩子函数,我们可以使用这些函数,在对象创建的不同阶段加上我们需要的代码,实现特定的功能。
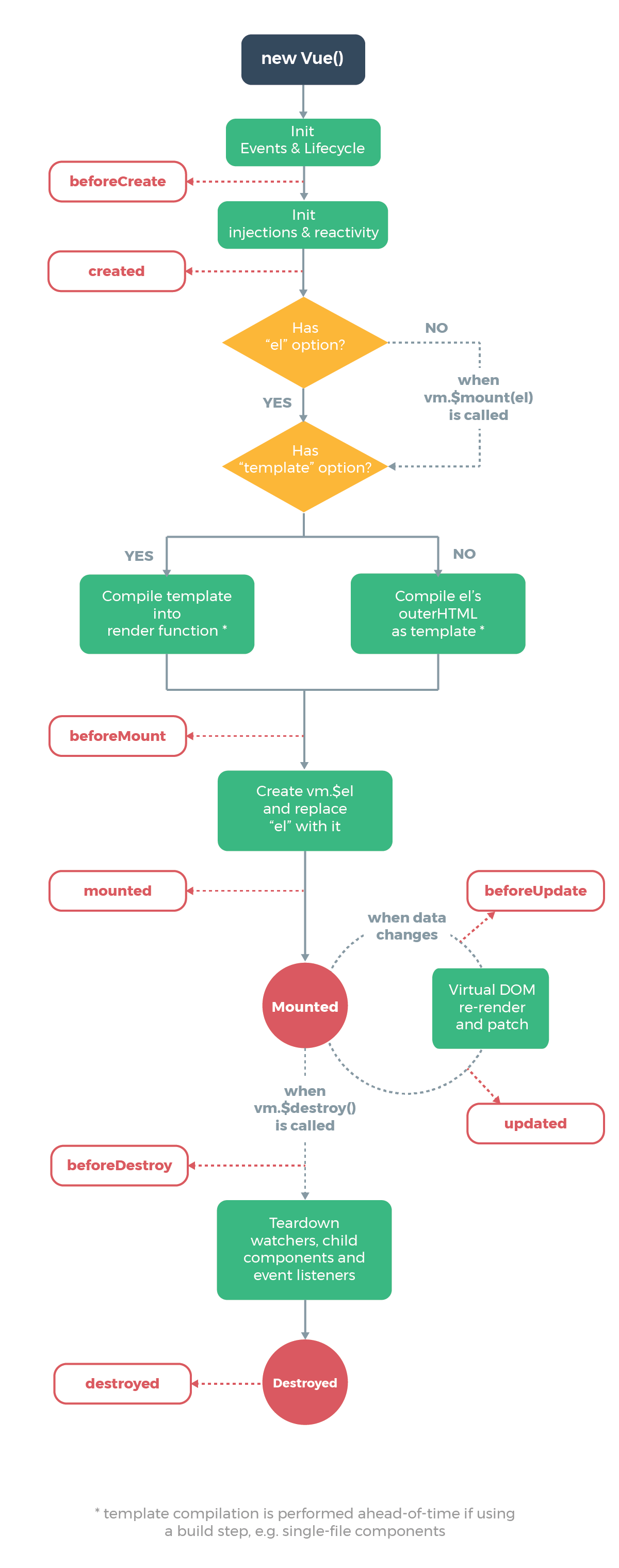
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
num:0
},
beforeCreate:function(){
console.log("beforeCreate,vm对象尚未创建,num="+ this.num);
this.name=10;
},
created:function(){
console.log("created,vm对象创建完成,设置好了要控制的元素范围,num="+this.num );
this.num = 20;
},
beforeMount:function(){
console.log( this.$el.innerHTML );
console.log("beforeMount,vm对象尚未把data数据显示到页面中,num="+this.num );
this.num = 30;
},
mounted:function(){
console.log( this.$el.innerHTML );
console.log("mounted,vm对象已经把data数据显示到页面中,num="+this.num);
},
beforeUpdate:function(){
console.log( this.$el.innerHTML );
console.log("beforeUpdate,vm对象尚未把更新后的data数据显示到页面中,num="+this.num);
},
updated:function(){
console.log( this.$el.innerHTML );
console.log("updated,vm对象已经把过呢更新后的data数据显示到页面中,num=" + this.num );
},
});
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{num}}</p>
<button @click="num++">按钮</button>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
总结:
1
2
3
4
| 在vue使用的过程中,如果要初始化操作,把初始化操作的代码放在 mounted 中执行。
mounted阶段就是在vm对象已经把data数据实现到页面以后。一般页面初始化使用。例如,用户访问页面加载成功以后,就要执行的ajax请求。
另一个就是created,这个阶段就是在 vue对象创建以后,把ajax请求后端数据的代码放进 created
|
阻止事件冒泡和刷新页面
件冒泡:指代js中子元素的事件触发以后,会导致父级元素的同类事件一并被触发到。
事件冒泡有好处,也有坏处。
好处:如果能正确利用这种现象,可以实现事件委托,提升特效的性能
坏处:如果没有正确使用,则会导致不必要的bug出现。
使用.stop和.prevent
原生js阻止事件冒泡
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>事件冒泡</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
background-color: orange;
padding-top: 100px;
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #000;
margin: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body onclick="alert('点击了body')">
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
<script>
var box1 = document.getElementsByClassName("box1")[0];
var box2 = document.getElementsByClassName("box2")[0];
box1.onclick = function(){
alert("点击了box1");
}
box2.onclick = function(event){
alert("点击了box2");
console.log(event);
event.stopPropagation();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
利用事件冒泡现象实现事件委托
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>事件冒泡</title>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="app">
<li>1111111111111111</li>
<li>2222222222222222</li>
<li>3333333333333333</li>
<li>4444444444444444</li>
<li>5555555555555555</li>
</ul>
<script>
// 批量元素绑定事件
// var list = document.getElementById("app").children;
// for(var i in list){
// list[i].onclick = function(){
// console.log(this.innerHTML);
// }
// }
// 可以通过事件委托来提升性能
var ul = document.getElementById("app");
ul.onclick = function(event){
// 事件最初的触发元素
var self = event.target;
console.log(self.innerHTML)
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
vue中阻止事件冒泡
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>事件冒泡</title>
<style>
.box1{
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
background-color: orange;
padding-top: 100px;
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #000;
margin: auto;
}
</style>
<script src="vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app" class="box1" @click="show('点击了box1')">
<div class="box2" @click.stop="show('点击了box2')"></div>
</div>
<script>
// vue本质上就是js,所以vue中的事件操作也会存在事件冒泡现象
// 可以使用辅助指令 @click.stop来阻止事件冒泡
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
methods:{
show(message){
alert(message);
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
综合案例-todolist
我的计划列表
html代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>todolist</title>
<style type="text/css">
.list_con{
width:600px;
margin:50px auto 0;
}
.inputtxt{
width:550px;
height:30px;
border:1px solid #ccc;
padding:0px;
text-indent:10px;
}
.inputbtn{
width:40px;
height:32px;
padding:0px;
border:1px solid #ccc;
}
.list{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
margin-top:20px;
}
.list li{
height:40px;
line-height:40px;
border-bottom:1px solid #ccc;
}
.list li span{
float:left;
}
.list li a{
float:right;
text-decoration:none;
margin:0 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="list_con">
<h2>To do list</h2>
<input type="text" name="" id="txt1" class="inputtxt">
<input type="button" name="" value="增加" id="btn1" class="inputbtn">
<ul id="list" class="list">
<li>
<span>学习html</span>
<a href="javascript:;" class="up"> ↑ </a>
<a href="javascript:;" class="down"> ↓ </a>
<a href="javascript:;" class="del">删除</a>
</li>
<li><span>学习css</span><a href="javascript:;" class="up"> ↑ </a><a href="javascript:;" class="down"> ↓ </a><a href="javascript:;" class="del">删除</a></li>
<li><span>学习javascript</span><a href="javascript:;" class="up"> ↑ </a><a href="javascript:;" class="down"> ↓ </a><a href="javascript:;" class="del">删除</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
特效实现效果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>todolist</title>
<style type="text/css">
.list_con{
width:600px;
margin:50px auto 0;
}
.inputtxt{
width:550px;
height:30px;
border:1px solid #ccc;
padding:0px;
text-indent:10px;
}
.inputbtn{
width:40px;
height:32px;
padding:0px;
border:1px solid #ccc;
}
.list{
margin:0;
padding:0;
list-style:none;
margin-top:20px;
}
.list li{
height:40px;
line-height:40px;
border-bottom:1px solid #ccc;
}
.list li span{
float:left;
}
.list li a{
float:right;
text-decoration:none;
margin:0 10px;
}
</style>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="todolist" class="list_con">
<h2>To do list</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="message" class="inputtxt">
<input type="button" @click="addItem" value="增加" class="inputbtn">
<ul id="list" class="list">
<li v-for="item,key in dolist">
<span>{{item}}</span>
<a @click="upItem(key)" class="up" > ↑ </a>
<a @click="downItem(key)" class="down"> ↓ </a>
<a @click="delItem(key)" class="del">删除</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#todolist",
data:{
message:"",
dolist:[
"学习html",
"学习css",
"学习javascript",
]
},
methods:{
addItem(){
if(this.messsage==""){
return false;
}
this.dolist.push(this.message);
this.message = ""
},
delItem(key){
this.dolist.splice(key, 1);
},
upItem(key){
if(key==0){
return false;
}
let result = this.dolist.splice(key,1);
this.dolist.splice(key-1,0,result[0]);
},
downItem(key){
let result = this.dolist.splice(key, 1);
console.log(result);
this.dolist.splice(key+1,0,result[0]);
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
