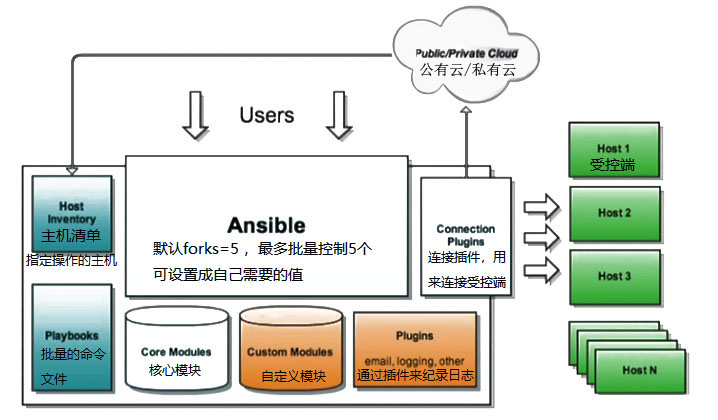
Ansible基础入门 Ansible基础概述 Ansible是一个自动化统一配置管理工具,自动化主要体现在Ansible集成了丰富模块以及功能组件,可以通过一个命令完成一系列的操作,进而能减少重复性的工作和维护成本,可以提高工作效率
同类型软件对比
对比
puppet
Ansible
Saltstack
开发语言
ruby
python
Python
远程执行功能
没有
有、串行
有、并行
客户端
没有
没有
有
架构
SSH
C/S、也支持SSH
Ansible的功能 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 1.远程执行 批量执行远程命令,可以对多台主机进行远程操作 2.配置管理 批。。34www量配置软件服务,可以进行自动化方式配置,服务的统一配置管理,和启停 3.事件驱动 通过Ansible的模块,对服务进行不同的事件驱动 比如: 1)修改配置后重启 2)只修改配置文件,不重启 3)修改配置文件后,重新加载 4)远程启停服务管理 4.管理公有云 通过API接口的方式管理公有云,不过这方面做的不如saltstack. saltstack本身可以通过saltcloud管理各大云厂商的云平台 5.二次开发 因为语法是Python,所以便于运维进行二次开发 6.任务编排 可以通过playbook的方式来统一管理服务,并且可以使用一条命令,实现一套架构的部署 123456789101112131415161718192021222324 7.跨平台,跨系统 几乎不受到平台和系统的限制,比如安装apache和启动+服务 在Ubuntu上安装apache服务名字叫apache23 在CentOS上安装apache服务名字叫httpd 在CentOS6上启动服务器使用命令:/etc/init.d/nginx start 在CentOS7上启动服务器使用命令:systemctl start nginx
Ansible的架构
连接插件connection plugins用于连接主机 用来连接被管理端
核心模块core modules连接主机实现操作, 它依赖于具体的模块来做具体的事情
自定义模块custom modules根据自己的需求编写具体的模块
插件plugins完成模块功能的补充
剧本playbookansible的配置文件,将多个任务定义在剧本中,由ansible自动执行
主机清单inventor定义ansible需要操作主机的范围
最重要的一点是 ansible是模块化的 它所有的操作都依赖于模块
Ansible的执行流程
Ansible读取playbook剧本,剧本中会记录对哪些主机执行哪些任务
首先Ansible通过主机清单找到要执行的主机,然后调用具体的模块
其次Ansible会通过连接插件连接对应的主机并推送对应的任务列表
最后被管理的主机会将Ansible发送过来的任务解析为本地Shell命令执行
Ansible安装部署 环境准备
主机名
WanIP
LanIP
角色
m01
10.0.0.61
172.16.1.61
Ansible控制端
web01
10.0.0.7
172.16.1.7
被控端
web02
10.0.0.8
172.16.1.8
被控端
安装Ansible
选项
说明
–version
ansible版本信息
-v
显示详细信息
-i
主机清单文件路径,默认是在/etc/ansible/hosts
-m
使用的模块名称,默认使用command模块
-a
使用的模块参数,模块的具体动作
-k
提示输入ssh密码,而不使用基于ssh的密钥认证
-C
模拟执行测试,但不会真的执行
-T
执行命令的超时
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] ansible 2.9.27 config file = ca configured module search path = [u'/root/.ansible/plugins/modules' , u'/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules' ] ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible executable location = /usr/bin/ansible python version = 2.7.5 (default, Oct 30 2018, 23:45:53) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-36)]
Ansible配置文件读取顺序
$ANSIBLE_CONFIG
.ansible.cfg
~/.ansible.cfg
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
Ansible配置文件详解 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 [root@m01 ~] host_key_checking = False log_path = /var/log /ansible.log [privilege_escalation]
Ansible Inventory(主机清单) /etc/ansible/hosts是ansible默认主机资产清单文件,用于定义被管理主机的认证信息, 例如ssh登录用户名、密码以及key相关信息。Inventory文件中填写需要被管理的主机与主机组信息。还可以自定义Inventory主机清单的位置,使用-i指定文件位置即可
使用IP+端口+用户+密码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 [root@m01 ~] [web_group] 10.0.0.7 ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass='123' 10.0.0.8 ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass='123' [root@m01 ~] 10.0.0.7 | SUCCESS => { "ansible_facts" : { "discovered_interpreter_python" : "/usr/bin/python" }, "changed" : false , "ping" : "pong" } 10.0.0.8 | SUCCESS => { "ansible_facts" : { "discovered_interpreter_python" : "/usr/bin/python" }, "changed" : false , "ping" : "pong" [root@m01 ~] 10.0.0.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda3 19G 1.5G 18G 8% / devtmpfs 476M 0 476M 0% /dev tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 487M 7.7M 479M 2% /run tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda1 497M 120M 378M 25% /boot tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0 10.0.0.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda3 19G 1.5G 18G 8% / devtmpfs 476M 0 476M 0% /dev tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 487M 7.7M 479M 2% /run tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda1 497M 120M 378M 25% /boot tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0
主机名+密码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 [root@m01 ~] [web_group] web0[1:2] ansible_ssh_pass='123' [root@m01 ~] 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 10.0.0.7 web01 10.0.0.8 web02 [root@m01 ~] web01 | SUCCESS => { "ansible_facts" : { "discovered_interpreter_python" : "/usr/bin/python" }, "changed" : false , "ping" : "pong" } web02 | SUCCESS => { "ansible_facts" : { "discovered_interpreter_python" : "/usr/bin/python" }, "changed" : false , "ping" : "pong" }
变量方式,主机名+密码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 [web_group] web0[1:2] [web_group:vars] ansible_ssh_pass='123' [root@m01 ~] 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 10.0.0.7 web01 10.0.0.8 web02
使用秘钥连接 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [web_group] 10.0.0.7:22 10.0.0.8:22 [root@manage01 ~] 10.0.0.8 | SUCCESS => { "ansible_facts" : { "discovered_interpreter_python" : "/usr/bin/python" }, "changed" : false , "ping" : "pong" } 10.0.0.7 | SUCCESS => { "ansible_facts" : { "discovered_interpreter_python" : "/usr/bin/python" }, "changed" : false , "ping" : "pong
企业使用究极进化版(☆☆☆☆☆) 1 2 3 4 [root@m01 ~] [web_group] web01 ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.7 ansible_ssh_port=22 web02 ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.8 ansible_ssh_port=22
配置主机标签组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 [标签组名字:children] 主机标签名1 主机标签名2 [lnmp:children] db_group web_group [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~]
Ansible执行任务
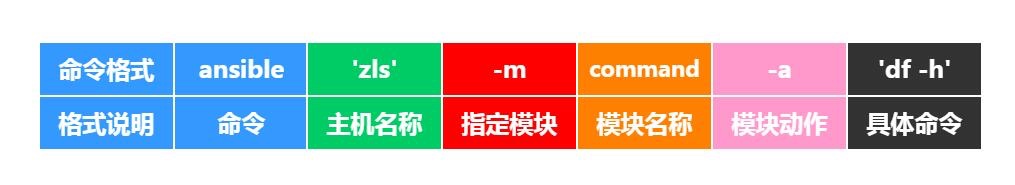
1 2 ad-hoc语法: ansible 主机 -m 模块 -a 动作
ad-hoc结果返回颜色
绿色:命令执行成功且无变化的颜色
黄色:命令执行成功,但是有变化(有更改)
红色:命令执行失败,报错msg
粉色|紫色:Warning,警告一般无需处理
ansible查看帮助 1 2 ansible-doc 模块名 找到帮助信息中的:EXAMPLES
Ad-hoc常用模块 command模块、shell模块 1 2 3 4 [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] 注意:command 模块不支持特殊符号
script模块 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] 优势:无需将脚本放在其他的机器上
Ansible文件管理模块 file模块 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 src:指定软链接的源文件 dest:指定软链接的目标文件 path:指定文件路径 owner:指定文件属主 group:指定文件属组 mode:指定文件权限 recurse:递归 state: - touch 创建文件 - absent 删除 - directory 创建目录 - link 软链接 - hard 硬链接 [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~]
copy模块 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 src:指定源文件的路径 dest:指定目标路径 owner:指定属主 group:指定属组 mode:指定权限 backup:备份 - yes 备份 True - no 不备份 False 默认 remote_src:远端的源文件 - yes/True - no/False content:指定内容写入文件(只能覆盖) [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~]
get_url 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 [root@m01 ~] url:下载的网址 dest:下载的路径 mode:指定权限 [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~]
Ansible软件管理模块 yum模块 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 [root@m01 ~] name:指定安装包的名字 - http:// 从指定的url下载 yum install -y http://网址 - file:// 从本地rpm包安装 yum localinstall - 包名 从yum仓库中下载 yum install -y 包名 state: - absent/removed:卸载 yum remove - present/installed:安装 yum install 默认 - latest:安装最新版本 download_only:只下载不安装 [root@m01 ~]
yum_repository 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 [root@m01 ~] [base] name=xxxx baseurl=http://xxx gpgcheck=0 gpgkey=file://xxx enable =1 name:仓库的名字[base] description:仓库的描述信息 name=xxxx baseurl:仓库的url地址 baseurl=http://xxx file:如果没有指定file则文件名和name指定的一致,如果指定了file,文件名为file指定的内容,仓库名为 name指定的内容 owner:指定属主 group:指定属组 mode:指定权限 gpgcheck:秘钥对检测 - yes/True gpgcheck=1 - no/False gpgcheck=0 enabled:是否开启仓库 - yes/True enable =1 - no/False enable =0 state: - present:创建仓库 - absent:删除仓库 [root@m01 ~] [root@web01 ~] [nginx-stable] baseurl = http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever /$basearch / enabled = 1 gpgcheck = 0 name = nginx stable repo [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~]
Ansible服务管理模块 service、systemd 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 [root@m01 ~] name:指定服务名字 state: - started 开启服务 - reloaded 重新加载服务 - stopped 停止服务 - restarted 重启服务 enabled:开机自启 - yes/True 加入开机自启 - no/False 不加入开机自启 默认 [root@m01 ~]
Ansible用户管理模块 user 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 [root@m01 ~] useradd www -u 666 -g 666 -s /sbin/nologin -M -c:描述信息 name:用户名 comment:-c:指定用户描述信息 uid:-u:指定用户的uid group: -g:指定用户的组 gid shell: -s:指定用户登录的shell -s /sbin/nologin append:-a:指定附加组并追加附加组 groups:-G:指定用户附加组 state: - absent 删除用户 userdel - present 创建用户 useradd 默认 remove: - yes/True userdel -r 删除用户和用户相关的文件 - no/False 默认 ssh_key_bits:创建用户时,创建私钥,私钥的位数 2048 ssh_key_file:指定私钥的位置 create_home: - yes/True 创建用户同时创建家目录 默认 - no/False 创建用户不创建家目录 [root@m01 ~]
group 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 [root@m01 ~] name:指定组名字 gid:指定组id state: - present 创建组 groupadd 默认 - absent 删除组 groupdel [root@m01 ~]
Ansible定时任务模块 cron 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 [root@m01 ~] 00 05 * * * /usr/bin/ntpdate time1.aliyun.com &>/dev/null name:定时任务注释信息 minute:分 00 hour:时 04 day:日 month:月 weekday:周 job:执行的任务 /bin/ls state: - present 创建定时任务 默认 - absent 删除定时任务 [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~]
Ansible磁盘挂载模块 mount 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 [root@m01 ~] mount -t nfs 172.16.1.31:/data /code/wordpress/wp-content/uploads path:挂载路径 /code/wordpress/wp-content/uploads src:挂载源 172.16.1.31:/data fstype:文件类型 -t nfs state: - present:只将挂载信息记录在/etc/fstab中(开机挂载) - mounted:立刻挂载,并将配置写入/etc/fstab中 - unmounted:卸载设备,但是不会清除/etc/fstab中的内容 - absent:卸载设备,并清除/etc/fstab中的内容 挂载:mounted 卸载:absent mount -o rw,remount / opts: 指定挂载路径是否可读可写 rw,remount [root@m01 ~]
Ansible解压模块 archive、unarchive 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 - name: 压缩yum源 archive: path: /etc/yum.repos.d/ dest: /tmp/yum.tgz remove: True src:指定压缩包路径 dest:指定解压的目标路径 owner:属主 group:数组 mode:权限 remote_src:告诉ansible压缩包在远端的服务器上 - yes/True - no/False 默认
Ansible数据库模块 mysql_user 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 [root@m01 ~] mysql -uroot -p123 grant all on *.* to wp_user@'%' identified by '123' ; name:指定用户名 wp_user host:指定允许连接的IP主机 % password:指定密码 123 priv:指定权限 '*.*:ALL' login_user:MySQL登录的用户 root login_password:MySQL登录用户root的密码 123 state: - present 创建 - absent 删除 vim /etc/my.cnf [mysqld] skip_name_resolve [root@db01 ~] [root@db01 ~]
mysql_db 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 [root@m01 ~] create database wordpress; mysqldump -uroot -p123 -B wordpress > /tmp/wordpress.sql name:指定库名 wordpress target:导出数据指定存放sql文件的路径 login_user:指定登录的用户 login_password:指定登录的密码 state: - present 创建 - absent 删除 - import 导入数据 - dump 导出数据
setup模块 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 [root@m01 ~] ansible_all_ipv4_addresses:仅显示ipv4的信息 ansible_devices:仅显示磁盘设备信息 ansible_distribution:显示是什么系统,例:centos,suse等 ansible_distribution_major_version:显示是系统主版本 ansible_distribution_version:仅显示系统版本 ansible_machine:显示系统类型,例:32位,还是64位 ansible_eth0:仅显示eth0的信息 ansible_hostname:仅显示主机名 ansible_kernel:仅显示内核版本 ansible_lvm:显示lvm相关信息 ansible_memtotal_mb:显示系统总内存 ansible_memfree_mb:显示可用系统内存 ansible_memory_mb:详细显示内存情况 ansible_swaptotal_mb:显示总的swap内存 ansible_swapfree_mb:显示swap内存的可用内存 ansible_mounts:显示系统磁盘挂载情况 ansible_processor:显示cpu个数(具体显示每个cpu的型号) ansible_processor_vcpus:显示cpu个数(只显示总的个数) ansible_hostname // 显示第一个.之前的主机名 ansible_fqdn // 显示完整的主机名 ansible_memtotal_mb // 总内存 ansible_memfree_mb // 空闲内存 ansible_swaptotal_mb // 总虚拟内存 ansible_swapfree_mb // 空闲虚拟内存 ansible_processor_cores // cpu核心数 ansible_os_family // 系统类型 RedHat Debain ansible_distribution // 系统发行版 CentOS ansible_distribution_major_version // 版本号 7 ansible_distribution_version // 详细版本号 7.6 ansible_dns.nameservers // DNS ansible_default_ipv4.address // eth0外网IP ansible_eth0.ipv4.address // eth0外网IP ansible_eth1.ipv4.address // eth1内网IP ansible_devices.sda.partitions.sda1.size // sda1分区的磁盘大小:/boot分区 ansible_devices.sda.partitions.sda3.size // sda3分区的磁盘大小: /分区
快速搭建rsync 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 uid = rsync gid = rsync port = 873 fake super = yes use chroot = no max connections = 200 timeout = 600 ignore errors read only = false list = false auth users = rsync_backup secrets file = /etc/rsync.passwd log file = /var/log /rsyncd.log [backup] comment = welcome to oldboyedu backup! path = /backup ansible web01 -m yum -a 'name=rsync' ansible web01 -m copy -a 'src=/root/rsyncd.conf dest=/etc/' ansible web01 -m copy -a 'content="rsync_backup:123456" dest=/etc/rsync.pass mode=600' ansible web01 -m group -a 'name=www gid=666' ansible web01 -m user -a 'name=www uid=666 group=666 shell=/sbin/nologin create_home=false' ansible web01 -m file -a 'path=/backup owner=www group=www state=directory' ansible web01 -m service -a 'name=rsyncd state=started enabled=true' ansible web02 -m yum -a 'name=rsync' ansible web02 -m copy -a 'content="123456" dest=/etc/rsync.pass mode=600'
作业 1.部署rsync
2.部署nfs
3.部署httpd,载上传作业的目录
准备工作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 uid = www gid = www port = 873 fake super = yes use chroot = no max connections = 200 timeout = 600 ignore errors read only = false list = false auth users = rsync_backup secrets file = /etc/rsync.passwd log file = /var/log /rsyncd.log [backup] comment = welcome to oldboyedu backup! path = /backup User www Group www [root@m01 web] [root@m01] [web_group] web01 ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.7 web02 ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.8 [nfs_group] nfs ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.31 [backup_group] backup ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.41 [rsyncd:children] nfs_group backup_group [root@m01] [root@m01] #!/bin/bash . /etc/init.d/functions ls -l ~/.ssh/id_rsa &>/dev/null || ssh-keygen -t rsa -P '' -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa &>/dev/null for n in 7 8 31 41;do sshpass -p 12 ssh-copy-id -o 'StrictHostKeyChecking no' -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@10.0.0.$n &>/dev/null && \ action "10.0.0.$n send public key " /bin/true || \ action "10.0.0.$n send public key " /bin/false done
环境准备
主机名
WanIP
LanIP
角色
应用
m01
10.0.0.61
172.16.1.61
ansible管理机
ansible
web01
10.0.0.7
172.16.1.7
作业网站
httpd、php、nfs
web02
10.0.0.8
172.16.1.8
作业网站
httpd、php、nfs
nfs
10.0.0.31
172.16.1.31
共享存储
nfs、rsync
backup
10.0.0.41
172.16.1.41
实时同步备份
nfs、rsync
编写Ad-hoc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 ansible all -m group -a 'name=www gid=666' ansible all -m user -a 'name=www uid=666 group=666 shell=/sbin/nologin create_home=false' ansible rsyncd -m yum -a 'name=rsync,nfs-utils state=present' ansible backup -m copy -a 'src=/root/web/rsyncd.conf dest=/etc/' ansible backup -m copy -a 'content=rsync_backup:123 dest=/etc/rsync.passwd mode=600' ansible backup -m file -a 'path=/backup owner=www group=www mode=755 state=directory' ansible backup -m service -a 'name=rsyncd state=started' ansible nfs -m copy -a 'content=123 dest=/etc/rsync.passwd mode=600' ansible nfs -m copy -a 'content="/data 172.16.1.0/24(rw,sync,anonuid=666,anongid=666,all_squash)" dest=/etc/exports' ansible nfs -m file -a 'path=/data owner=www group=www mode=755 state=directory' ansible nfs -m service -a 'name=nfs state=started' ansible web_group -m yum -a 'name=httpd,php state=present' ansible web_group -m copy -a 'src=/root/web/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf' ansible web_group -m unarchive -a 'src=/root/web/kaoshi.tgz dest=/var/www/html owner=www group=www' ansible web_group -m file -a 'path=/var/www/html/user_data owner=www group=www state=directory' ansible web_group -m mount -a 'src=172.16.1.31:/data fstype=nfs path=/var/www/html/user_data state=mounted' ansible web_group -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started'
Ansible剧本playbook
Q:什么是playbook?
playbook:剧本,兵书之意
playbook是由什么组成
playbook语法 yaml语法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 - hosts: web_group remote_user: root tasks: - name: install httpd and php yum: - httpd - php - name: configure httpd conf copy: src: /root/web/httpd.conf dest: /etc/httpd/conf
ansible 写playbook后缀 .yml 或者 .yaml
saltstack 写sls文件 后缀 .sls
playbook小练习 安装httpd
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ansible] - hosts: web_group tasks: - name: Install httpd yum: name: httpd state: present [root@m01 ansible] [root@m01 ansible] [root@m01 ansible]
启动httpd并加入开机自启
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 - hosts: web_group tasks: - name: Install httpd yum: name: httpd state: present - name: Start httpd Service service: name: httpd state: started enabled: True
编写http前端页面
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 [root@m01 ansible] - hosts: web_group tasks: - name: Install httpd yum: name: httpd state: present - name: Start httpd Service service: name: httpd state: started enabled: True - name: Set Web Index copy: content: roger_http_web dest: /var/www/html/index.html
不同的主机配置不同的网站
目前来说,想要根据不同主机配置不同的网站,我们可以使用多个play的方式,但是在生产环境中,我们需要写循环,来满足我们的需求,多个play了解即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 [root@m01 ansible] - hosts: web_group tasks: - name: Install httpd yum: name: httpd state: present - name: Start httpd Service service: name: httpd state: started enabled: True - hosts: web01 tasks: - name: Set Web01 Index copy: content: roger_http_web01 dest: /var/www/html/index.html - hosts: web02 tasks: - name: Set Web01 Index copy: content: roger_http_web02 dest: /var/www/html/index.html
playbook实战 1.部署rsync
2.部署nfs
3.部署httpd,载上传作业的目录
环境准备
主机名
WanIP
LanIP
角色
应用
m01
10.0.0.61
172.16.1.61
ansible管理机
ansible
web01
10.0.0.7
172.16.1.7
作业网站
httpd、php、nfs
web02
10.0.0.8
172.16.1.8
作业网站
httpd、php、nfs
nfs
10.0.0.31
172.16.1.31
共享存储
nfs、rsync
backup
10.0.0.41
172.16.1.41
实时同步备份
nfs、rsync
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 [root@m01 web] total 44 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 11753 Jun 28 16:41 httpd.conf -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 26868 Jun 28 16:52 kaoshi.tgz -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 336 Jun 27 20:35 rsyncd.conf [root@m01 ansible] - hosts: all tasks: - name: Create www group group: name: www gid: 666 - name: Create www user user: name: www uid: 666 group: '666' shell: /sbin/nologin create_home: False - hosts: rsyncd tasks: - name: Install rsync,nfs-utils Service yum: name: - rsync - nfs-utils state: present - hosts: backup tasks: - name: Configure rsync Conf copy: src: /root/web/rsyncd.conf dest: /etc/ - name: Configure rsync.passwd File copy: content: rsync_backup:123 dest: /etc/rsync.passwd mode: 0600 - name: Create backup Directory file: path: /backup owner: www group: www mode: 0755 state: directory - name: Start rsync Service service: name: rsyncd state: started enabled: True - hosts: nfs tasks: - name: Create Client rsync.passwd File copy: content: 123 dest: /etc/rsync.passwd mode: 0600 - name: Configure nfs Conf copy: content: "/data 172.16.1.0/24(rw,sync,anonuid=666,anongid=666,all_squash) dest: /etc/exports - name: Create nfs Directory file: path: /data owner: www group: www mode: 0755 state: directory - name: Start nfs Service service: name: nfs state: started enabled: True - hosts: web_group tasks: - name: Install httpd,php Service yum: name: - httpd - php state: present - name: Configure httpd Conf copy: src: /root/web/httpd.conf dest: /etc/httpd/conf - name: Unarchive php Service unarchive: src: /root/web/kaoshi.tgz dest: /var/www/html owner: www group: www - name: Deplay kaoshi Code unarchive: src: /root/web/kaoshi.tgz dest: /var/www/html owner: www group: www - name: Create user_data Directory file: path: /var/www/html/user_data owner: www group: www mode: 0755 state: directory - name: Mount user_data Directory mount: src: 172.16.1.31:/data path: /var/www/html/user_data fstype: nfs state: mounted - name: Start httpd Service service: name: httpd state: started enabled: True stat -c %a /var/www/html/user_data/
playbook部署wordpress
主机名
WanIP
LanIP
角色
应用
m01
10.0.0.61
172.16.1.61
ansible管理机
ansible
web01
10.0.0.7
172.16.1.7
wordpress
httpd、php、nfs
web02
10.0.0.8
172.16.1.8
wordpress
httpd、php、nfs
nfs
10.0.0.31
172.16.1.31
共享存储
nfs、rsync
backup
10.0.0.41
172.16.1.41
实时同步备份
nfs、rsync
db01
10.0.0.51
172.16.1.51
数据库
MariaDB、MySQL-python
准备工作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 [root@m01 ~] /root/wordpress_ansible/ ├── base │ ├── hosts │ └── ssh_key.sh ├── lnmp.yml ├── mariadb │ ├── my.cnf │ └── wp_ansible.sql ├── nfs │ └── 2022.tgz ├── nginx_php │ ├── blog.roger.com.conf │ ├── nginx.conf │ ├── nginx_php.tgz │ └── www.conf ├── rsync │ └── rsyncd.conf ├── test.yml ├── wordpress │ └── wordpress.tgz [root@m01 ngx_php] [root@m01 ngx_php] [root@m01 ngx_php] user www; [root@m01 ngx_php] [root@m01 ngx_php] [www] user = www group = www listen = /dev/shm/php.sock listen.owner = www listen.group = www [root@m01 ngx_php] [root@m01 ngx_php] server { listen 80; server_name blog.roger.com; root /code/wordpress; index index.php index.html; location ~ \.php$ { fastcgi_pass unix:/dev/shm/php.sock; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root $fastcgi_script_name ; include fastcgi_params; } } [root@m01 ngx_php] [root@m01 ngx_php] [root@m01 ngx_php] [root@m01 ngx_php]
数据备份 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 [root@m01 code] [root@db01 ~] [root@db01 ~] [root@m01 code] [root@m01 code] uid = www gid = www port = 873 fake super = yes use chroot = no max connections = 200 timeout = 600 ignore errors read only = false list = false auth users = rsync_backup secrets file = /etc/rsync.passwd log file = /var/log /rsyncd.log [backup] comment = welcome to oldboyedu backup! path = /backup
lnmp.yml 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 - hosts: all tasks: - name: 创建www组 group: name: www gid: 666 - name: 创建www用户 user: name: www uid: 666 group: 666 shell: /sbin/nologin create_home: False - name: 更新yum缓存 shell: yum makecache - hosts: rsyncd tasks: - name: 安装rsync, nfs-utils服务 yum: name: - rsync - nfs-utils state: present - hosts: backup_group tasks: - name: 创建backup目录 file: path: /backup owner: www group: www mode: 0755 state: directory - name: 推送rsync配置文件 copy: src: /root/ansible_wordpress/rsync/rsyncd.conf dest: /etc - name: 创建rsync密码文件 copy: content: 'rsync_backup:123' dest: /etc/rsync.passwd mode: 0600 - name: 启动rsync服务 service: name: rsyncd state: started enabled: True - hosts: nfs_group tasks: - name: 创建data目录 file: path: /data owner: www group: www mode: 0755 state: directory - name: 创建rsync密码文件 copy: content: '123' dest: /etc/rsync.passwd mode: 0600 - name: 修改nfs配置文件 copy: content: '/data 172.16.1.0/24(rw,sync,anonuid=666,anongid=666,all_squash)' dest: /etc/exports - name: 解压静态图片 unarchive: src: /root/ansible_wordpress/nfs/2023.tar.gz dest: /data owner: www group: www mode: 0755 - name: 启动nfs服务 service: name: nfs state: started enabled: True - hosts: web_group tasks: - name: 安装nfs-utils yum: name: nfs-utils state: present - name: 创建站点目录 file: path: /code owner: www group: www mode: 0755 state: directory - name: 推送nginx,php安装包 unarchive: src: /root/ansible_wordpress/nginx_php/nginx_php.tgz dest: /code - name: 安装nginx,php服务 shell: 'cd /code && yum localinstall -y *.rpm' - name: 推送nginx.conf配置 copy: src: /root/ansible_wordpress/nginx_php/nginx.conf dest: /etc/nginx - name: 推送nginx配置 copy: src: /root/ansible_wordpress/nginx_php/blog.roger.com.conf dest: /etc/nginx/conf.d - name: 推送php配置 copy: src: /root/ansible_wordpress/nginx_php/www.conf dest: /etc/php-fpm.d - name: 部署wordpress unarchive: src: /root/ansible_wordpress/wordpress/wordpress.tar.gz dest: /code - name: 挂载共享目录 mount: src: 172.16.1.31:/data path: /code/wordpress/wp-content/uploads fstype: nfs state: mounted - name: 启动nginx服务 service: name: nginx state: started enabled: True - name: 启动php-fpm服务 service: name: php-fpm state: started enabled: True - hosts: db_group tasks: - name: 安装mariadb服务 yum: name: - mariadb-server - MySQL-python state: present - name: 推送maridb配置 copy: src: /root/ansible_wordpress/maridb/my.cnf dest: /etc - name: 启动mariadb服务 service: name: mariadb state: started enabled: True - name: 创建wordprss数据库 mysql_db: login_user: root login_password: 123 name: wordpress state: present - name: 推送wordprss数据 copy: src: /root/ansible_wordpress/maridb/wordpress.sql dest: /opt - name: 导入wordprss数据 mysql_db: login_user: root login_password: 123 name: wordpress target: /opt/wordpress.sql state: import - name: 创建wordpress用户 mysql_user: login_user: root login_password: 123 name: wp_user password: 123 host: '%' priv: '*.*:ALL' state: present - name: 启动mariadb服务 service: name: mariadb state: started enabled: True
Ansible变量 变量的概述 避免重复代码,方便维护,减少维护成本
Ansible变量定义
命令行
play中定义
Inventory中定义
hosts文件
host_vars目录
group_vars目录
优先级 命令行 > play > inventory
命令行 > vars_files(play) > vars(play) > host_vars(inventory) > group_vars(inventory) > hosts文件(inventory)
定义Ansible变量位置 在play中定义变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 - hosts: web_group vars: user_group: huanglong id: '438' pkg: - nginx - php - mariadb-server tasks: - name: 创建{{ user_group }}组 group: name: "{{ user_group }}" gid: "{{ id }}" - name: 创建{{ user_group }}用户 user: name: "{{ user_group }}" uid: "{{ id }}" group: "{{ id }}" shell: /sbin/nologin create_home: False - name: 安装nginx php mysql yum: name: "{{ pkg }}" state: present
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 - hosts: web_group vars: user_group: huanglong id: '438' pkg: - nginx - php - mariadb-server vars_files: ./roger_var.yml tasks: - name: 创建{{ user_group }}组 group: name: "{{ user_group }}" gid: "{{ id }}" - name: 创建{{ user_group }}用户 user: name: "{{ user_group }}" uid: "{{ id }}" group: "{{ id }}" shell: /sbin/nologin create_home: False roger_var.yml user_group: wuyangke id: '250' pkg: - nginx - php - mariadb-server
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 jiagou: - lnmp: pkg: - nginx - php - mysql - lamp: pkg: - httpd - php - mysql - lamt: pkg: - httpd - tomcat - mysql - hosts: web_group tasks: - name: 安装lamt yum: name: "{{ jiagou.lamt.pkg }}"
在inventory中定义变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 [root@m01 ~] [web_group] web01 ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.7 web02 ansible_ssh_host=10.0.0.8 [web_group:vars] user_group=xxx id='666'
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 mkdir host_vars vim host_vars/web01 user_group: user_host_vars_web01 id: '444'
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 mkdir group_vars vim group_vars/web_group user_group: user_group_vars_web_group id: '444'
优先级测试 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 vars:vars_user vars_files:user_vars_files - hosts: web_group vars: - user_group: vars_user - id: '444' vars_files: ./roger_var.yml tasks: - name: 创建用户 user: name: "{{ user_group }}" uid: "{{ id }}" state: present hosts文件中:user_inventory [web_group:vars] user_group=user_inventory host_vars目录下 - web01 user_group: user_host_vars_web01 - web02 user_group: user_host_vars_web02 group_vars目录下 web_group user_group: user_group_vars_web_group [root@m01 wordpress_ansible] [root@m01 wordpress_ansible]
变量注册 当absible的模块在运行之后,其实都会返回一些result结果,就像是执行脚本,我们有的时候需要脚本给我们一些return返回值,我们才知道,上一步是否可以执行成功,但是…默认情况下,ansible的result并不会显示出来,所以,我们可以把这些返回值’存储’到变量中,这样我们就能通过’调用’对应的变量名,从而获取到这些result,这种将模块的返回值,写入到变量中的方法被称为变量注册
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 - hosts: web_group tasks: - name: 查看nginx目录 shell: "ls -l /etc/nginx" register: xxx - name: 获取注册的变量值 nginx目录返回记过 debug: msg: "{{ xxx }}"
只需要打印详细的结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 - hosts: web_group tasks: - name: 查看nginx目录 shell: "ls -l /etc/nginx" register: xxx - name: 获取注册的变量值 nginx目录返回记过 debug: msg: "{{ xxx.stdout_lines }}"
利用变量注册做判断
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 - hosts: web_group tasks: - name: 查看nginx目录 shell: "ls -l /etc/nginx" register: xxx - name: 获取注册的变量值 nginx目录返回结果 debug: msg: "{{ xxx.stdout_lines }}" - name: 安装nginx和php shell: cd /opt && rpm -Uvh *.rpm when: xxx.rc != 0
facts缓存 Ansible facts是在被管理追击上通过Ansible自动采集发现的变量。facts包含每台特定的主机信息。比如:被控端的主机名、IP地址、系统版本、CPU数量、内存状态、磁盘状态等等。
facts缓存应用场景
关闭facts缓存 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 - hosts: rsync_nfs gather_facts: False tasks: - name: 安装rsync和nfs服务 yum: name: - rsync - nfs-utils state: present - name: 创建目录 file: path: /tmp/{{ ansible_memtotal_mb }} state: directory
Ansible流程控制 条件语句(判断) 当满足什么条件时,就执行哪些tasks
when 当….时
ansible获取主机名 1 2 3 ansible_hostname ansible_fqdn
不管是shell还是各大编程语言中,流程控制,条件判断这些都是必不可少的,在我们使用Ansible的过程中,条件判断的使用频率极其高。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 centos安装apache: yum install -y httpd unbuntu安装apache: apt-get install apache2 tasks: - name: "shut down Debian flavored systems" command : /sbin/shutdown -t now when: ansible_facts['os_family' ] == "Debian" tasks: - name: "shut down Debian flavored systems" command : apt-get install apache2 when: ansible_os_family == "Ubuntu" - hosts: rsync_nfs tasks: - name: 创建目录 file: path: /usr/local /{{ ansible_facts['default_ipv4' ]['address' ] }} state: directory
2.在nfs和rsync安装过程中,客户端服务器不需要推送配置文件,之前我们都是写多个play,会影响效率。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 - hosts: rsync_nfs tasks: - name: 安装rsync和nfs服务 yum: name: - rsync - nfs-utils state: present - name: 推送rsync配置文件 template: src: /root/wordpress_ansible/rsync/rsyncd.conf dest: /etc when: ansible_hostname == 'backup' - hosts: rsync_nfs tasks: - name: 安装rsync和nfs服务 yum: name: - rsync - nfs-utils state: present when: ansible_hostname == 'backup' or ansible_hostname == 'nfs' - name: 推送rsync配置文件 template: src: /root/wordpress_ansible/rsync/rsyncd.conf dest: /etc when: ansible_hostname == 'backup'
3.我们在源码安装nginx的时候,执行第二遍就无法执行了,此时我们就可以进行判断是否安装过。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 - hosts: web_group tasks: - name: 查看nginx目录 shell: "ls -l /etc/nginx" register: xxx - name: 判断是否安装nginx shell: 'cd /opt && rpm -Uvh *.rpm' when: xxx.rc != 0 and or ! tasks: - name: "shut down CentOS 6 systems" command : /sbin/shutdown -t now when: - ansible_facts['distribution' ] == "CentOS" - ansible_facts['distribution_major_version' ]|int == 6 - hosts: all tasks: - name: 推送nginx虚拟主机配置文件 copy: src: /root/wordpress_ansible/nginx_php/blog.zls.com.conf dest: /etc/nginx/conf.d when: ansible_hostname is match 'web*' - name: 推送php配置文件 copy: src: /root/wordpress_ansible/nginx_php/www.conf dest: /etc/php-fpm.d
playbook循环语句 在之前的学习过程中,我们经常会有传送文件,创建目录之类的操作,创建2个目录就要写两个file模块来创建,如果要创建100个目录,我们需要写100个file模块???妈耶~ 当然不是,只要有循环即可,减少重复性代码
列表循环 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 数据类型:列表 for 循环列表类型- hosts: all tasks: - name: 启动nginx 和 php service: name: "{{ item }}" state: stopped with_items: - nginx - php-fpm when: ansible_hostname is match 'web*' 注意:一般不用于循环配置文件
字典循环 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 - hosts: all tasks: - name: 启动nginx 和 php service: name: "{{ item }}" state: stopped with_items: - nginx - php-fpm when: ansible_hostname is match 'web*' - name: 推送nginx主配置文件、nginx虚拟主机配置文件和php配置文件 template: src: "{{ item.src }}" dest: "{{ item.dest }}" with_items: - {src: "/root/wordpress_ansible/nginx_php/blog.zls.com.conf" ,dest: "/etc/nginx/conf.d" } - {src: "/root/wordpress_ansible/nginx_php/nginx.conf" ,dest: "/etc/nginx" } when: ansible_hostname is match 'web*'
playbook handlers(触发器) 当修改完某个服务的配置文件时,应该重启该服务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 - hosts: all tasks: - name: 推送nginx和php的配置文件 template: src: "{{ item.src }}" dest: "{{ item.dest }}" with_items: - {src: "/root/wordpress_ansible/nginx_php/blog.zls.com.conf" ,dest: '/etc/nginx/conf.d' } - {src: "/root/wordpress_ansible/nginx_php/nginx.conf" ,dest: '/etc/nginx' } notify: Restart Nginx xxx when: ansible_hostname is match 'web*' - name: 启动nginx服务 service: name: nginx state: started enabled: True when: ansible_hostname is match 'web*' - name: 推送php配置文件 template: src: /root/wordpress_ansible/nginx_php/www.conf dest: /etc/php-fpm.d notify: aaa when: ansible_hostname is match 'web*' handlers: - name: Restart Nginx xxx service: name: nginx state: restarted - name: aaa service: name: php-fpm state: restarted
handler注意点
1.无论多少个task调用相同handler,只会在所有tasks执行完成后,触发一次handlers
2.Handlers只有在其所在的任务被执行时,才会被运行;如果一个任务中定义了notify调用Handlers,但是由于条件判断等原因,该任务未被执行,那么Handlers同样不会被执行
3.Handlers只会在每一个play的末尾运行一次;如果想在一个playbook中间运行Handlers,则需要使用meta模块来实现。例如: -meta: flush_handlers。
4.如果一个play在运行到调用Handlers的语句之前失败了,那么这个Handlers将不会被执行。我们可以使用meta模块的–force-handlers选项来强制执行Handlers,即使Handlers所在的play中途运行失败也能执行。
5.不能使用handlers替代tasks
Ansible任务标签 默认情况下,Ansible在执行一个playbook时,会执行playbook中定义的所有任务,Ansible的标签(tag)功能可以给单独任务甚至整个playbook打上标签,然后利用这些标签来指定要运行playbook中的个别任务,或不执行指定的任务
打标签的方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 - name: 安装rsync yum: name: rsync state: present when: ansible_hostname != 'db01' tags: install_rsync
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 - name: 推送rsync配置文件 template: src: /root/wordpress_ansible/rsync/rsyncd.conf dest: /etc when: ansible_hostname == 'backup' notify: Rrestart rsync tags: - install_rsync - send_rsync_config
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 - name: 安装rsync yum: name: rsync state: present when: ansible_hostname != 'db01' tags: install_rsync - name: 推送rsync配置文件 template: src: /root/wordpress_ansible/rsync/rsyncd.conf dest: /etc when: ansible_hostname == 'backup' tags: install_rsync - name: 创建密码文件 copy: content: "{{ rsync_user }}:123" dest: "{{ rsync_pass_path }}" mode: 0600 when: ansible_hostname == 'backup' tags: install_rsync - name: 创建{{ backup_dir }}目录 file: path: /{{ backup_dir }} owner: "{{ user_group }}" group: "{{ user_group }}" state: directory when: ansible_hostname == 'backup' tags: install_rsync - name: 启动rsync服务 service: name: rsyncd state: started enabled: True when: ansible_hostname == 'backup' tags: install_rsync
打完标签如何使用 -t:执行指定的tag标签任务
–skip-tags:执行–skip-tags之外的标签任务
1 2 ansible-playbook -i base/hosts lnmp_wp.yml -t 'install_rsync' ansible-playbook -i base/hosts lnmp_wp.yml --skip-tags 'install_rsync'
playbook的复用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 - hosts: all tasks: - include: nginx/install_nginx.yml - include: nginx/start_nginx.yml - include: php/install_php.yml handlers: - include: php/handler_php.yml php/config_php.yml - name: xxx template: src: xxx dest: xxx when: ansible_hostname is match 'web*' notify: restart php php/handler_php.yml - name: restart php service: name: php-fpm state: restarted
Jinja2 模板
Q:什么是Jinja2?
jinja2是Python的全功能模板引擎
Jinja2模板和Ansible关系 Ansible通常会使用jinja2模板来修改被管理主机的配置文件等…在saltstack中同样会使用到jinja2
1 2 3 4 5 upstram www.zls.com { server 172.16.1.7; server 172.16.1.8; server 172.16.1.9; }
Jinja2模板基础语法 1 2 {{ 变量名 }} ## 调用变量 {# 注释 #}
Jinja2判断语法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 ## shell判断 if [ 条件 ];then xxx elif [ 条件 ];then aaa else bbb fi ## Python判断 if 条件: xxx elif 条件: aaa else: bbb xxxx ## Jinja2判断 {% if 条件 %} xxx {% elif 条件 %} aaa {% else %} bbb {% endif %}
Jinja2循环 1 2 3 {% for n in 条件 %} xxx {% endfor %}
Jinja2实战部署keepalived 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 global_defs { router_id lb01 } vrrp_script check_web_zls { script "/root/check_web.sh" interval 5 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state MASTER interface eth0 virtual_router_id 50 priority 150 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 10.0.0.3 } track_script { check_web_zls } } global_defs { router_id lb02 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { priority 100 state BACKUP interface eth0 virtual_router_id 50 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 10.0.0.3 } } tasks.yml - hosts: all tasks: - include: /root/ansible/keepalived/config_keepalived.yml when: ansible_hostname is match 'web*' handlers: - name: Restart Keepalived service: name: keepalived keepalived.j2 global_defs { router_id {{ ansible_hostname }} } {% if ansible_hostname == 'web01' %} vrrp_script check_web_zls { script "/root/check_web.sh" interval 5 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { track_script { check_web_zls } priority 150 state MASTER {% else %} vrrp_instance VI_1 { priority 100 state BACKUP {% endif %} interface eth0 virtual_router_id 50 advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 10.0.0.3 } }
Jinja2实战部署负载均衡 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 upstream {{ wordpress_domain }} { {% for num in range(7,10) %} server 172.16.1.{{ num }}; {% endfor %} } server{ listen 80; server_name {{ wordpress_domain }}; location /{ proxy_pass http://{{ wordpress_domain }}; } } - hosts: all tasks: - include: /root/ansible/lb/config_lb.yml when: ansible_hostname is match 'web*'
Ansible Roles roles目录结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 production staging group_vars/ group1.yml group2.yml host_vars/ hostname1.yml hostname2.yml library/ module_utils/ filter_plugins/ site.yml webservers.yml dbservers.yml roles/ common/ tasks/ main.yml handlers/ main.yml templates/ ntp.conf.j2 files/ bar.txt foo.sh vars/ main.yml defaults/ main.yml meta/ main.yml library/ module_utils/ lookup_plugins/ webtier/ monitoring/ fooapp/
Ansible Galaxy创建目录 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 roles] - Role nginx was created successfully [root@m01 roles] total 0 drwxr-xr-x 10 root root 154 Jul 4 10:29 nginx [root@m01 roles] nginx/ ├── defaults │ └── main.yml ├── files ├── handlers │ └── main.yml ├── meta │ └── main.yml ├── README.md ├── tasks │ └── main.yml ├── templates ├── tests │ ├── inventory │ └── test.yml └── vars └── main.yml
使用roles重构rsync 创建项目 1 2 3 4 5 [root@m01 roles] - Role rsync-client was created successfully [root@m01 roles] - Role rsync-server was created successfully
rsync-server 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 [root@m01 ansible] /root/roles/rsync-server/ ├── defaults │ └── main.yml ├── files ├── handlers │ └── main.yml ├── meta │ └── main.yml ├── README.md ├── tasks │ ├── config_rsync.yml │ ├── main.yml │ ├── server_rsync.yml │ └── start_rsync.yml ├── templates │ └── rsyncd.j2 ├── tests │ ├── inventory │ └── test.yml └── vars └── main.yml [root@m01 ansible] uid = {{ user_group }} gid = {{ user_group }} port = 873 fake super = yes use chroot = no max connections = 200 timeout = 600 ignore errors read only = false list = false auth users = {{ rsync_user }} secrets file = {{ rsync_pass_file }} log file = /var/log /rsyncd.log[{{ rsync_dir }}] comment = welcome to oldboyedu backup! path = /{{ rsync_dir }} [{{ nfs_dir }}] comment = welcome to oldboyedu backup! path = /{{ nfs_dir }} [root@m01 ansible] - name: 推送rsync配置文件 template: src: rsyncd.j2 dest: /etc/rsyncd.conf notify: Restart Rsync [root@m01 ansible] - name: 创建密码文件 copy: content: "{{ rsync_user }}:{{ rsync_pass }}" dest: /{{ rsync_pass_file }} mode: 0600 - name: 创建rsync目录 file: path: "{{ item }}" owner: "{{ user_group }}" group: "{{ user_group }}" state: directory with_items: - /{{ rsync_dir }} - /{{ nfs_dir }} [root@m01 ansible] - name: 启动rsync service: name: rsyncd state: started enabled: True [root@m01 ansible] --- - include: config_rsync.yml - include: server_rsync.yml - include: start_rsync.yml [root@m01 ansible] dependencies: - {role: create-user} - {role: rsync-client} [root@m01 ansible] --- - name: Restart Rsync service: name: rsyncd state: restarted
系统优化 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 - name: 压缩yum源 archive: path: /etc/yum.repos.d/ dest: /tmp/yum.tgz remove: True - name:优化文件描述符 pam_limits: domain: '*‘ limit_type: ' -' limit_item: nofile value: ' 65535'
Ansible galaxy Ansible查找roles 1 2 [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~]
查看详细信息 1 2 [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~]
安装项目 Ansible vault 给playbook加密
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 [root@m01 ~] New Vault password: Confirm New Vault password: Encryption successful [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] Vault password: New Vault password: Confirm New Vault password: Rekey successful [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~] [root@m01 ~]